Diet And Evolution Of Human Amylase Gene
Diet and the evolution of human amylase gene copy number variation article perry2007dietat title diet and the evolution of human amylase gene copy number variation author g.
Diet and evolution of human amylase gene. Authors george h perry 1. Epub 2007 sep 9. Dominy and katrina g claw and a. Students analyze data on the number of copies of the salivary amylase amy1 gene among different human populations.
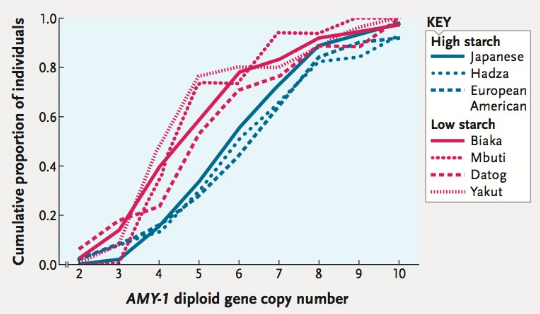
Diet and the evolution of human amylase gene copy number variation. Gene amy1 which kickstarts digestion of starch in the mouth is associated with blood glucose levels and digestion of carbohydrates with implications for understanding human evolutionary biology. Diet and the evolution of human amylase gene copy number variation nat genet. Starch consumption is a prominent characteristic of agricultural societies and hunter gatherers in arid environments.
This activity engages students in analyzing authentic scientific data that explore the effects of different diets on the evolution of an enzyme that breaks down starch. Diet and the evolution of human amylase gene copy number variation george h perry1 2 nathaniel j dominy3 katrina g claw1 4 arthur s lee2 heike fiegler5 richard redon5 john werner4 fernando avillanea3 joanna l mountain6 rajeev misra4 nigel p carter5 charles lee2 7 8 anne c stone1 8 starch consumption is a prominent characteristic of. Werner and fernando a. The human salivary amylase gene amy1 originated from duplication of the pancreatic amylase gene amy2 and its copy number is positively correlated with dietary starch levels the primary.